 Tue, 17 Jun 2025
Tue, 17 Jun 2025
What is Import and Export? A Beginners Guide
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how smartphones from South Korea or coffee beans from Brazil end up on your local store shelves? This is made possible through import and export — the foundation of global trade. At NaviExports.com, we simplify international trade concepts for beginners and business owners. In this guide, we’ll explore what import and export really mean, how they work, why they’re vital for economies, and how you can begin your journey in global commerce.
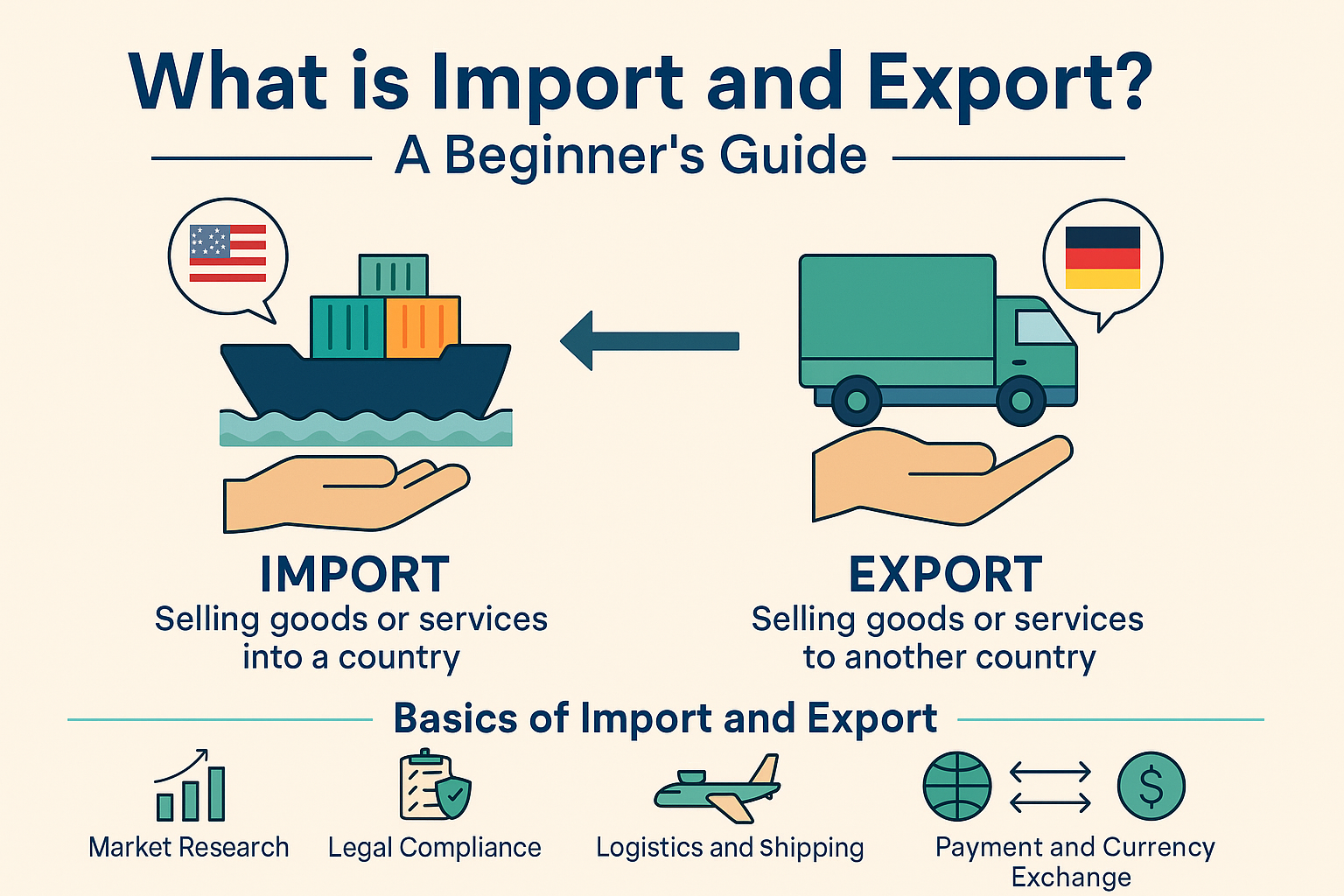
What is Import and Export?
-
Import refers to the process of bringing goods or services into a country from abroad for resale, manufacturing, or internal use.
-
Export involves sending goods or services from your country to another with the intention of selling them internationally.
Together, these transactions form the backbone of international trade and connect global markets.
Real-Life Examples
-
When a company in India imports machinery from Germany, it’s an import.
-
When the same company exports spices to the USA, that’s an export.
These daily exchanges span industries like electronics, agriculture, textiles, and automobiles.
Why Are Import and Export Important?
Import and export drive economic development and open new business opportunities. Here's why they matter:
-
Access to Diverse Products: Imports provide access to goods not produced domestically (e.g., avocados in Europe).
-
Boost to National Economy: Exports increase foreign earnings and create local jobs.
-
Competitive Advantage: Encourages innovation, cost reduction, and better-quality products.
-
Specialization and Efficiency: Countries can focus on what they produce best and trade for the rest.
-
Cultural and Technological Exchange: Trade introduces new ideas, products, and skills across borders.
How Does Import and Export Work?
Navigating international trade may seem complex, but it's manageable when broken into these key steps:
1. Market Research and Feasibility Study
Start by identifying demand, regulations, and competitor presence. Use resources like:
-
Trade portals
-
Government export databases
-
Industry reports
Example: Planning to export organic honey? Research demand in high-income, health-conscious markets like Japan or Germany.
2. Legal Requirements and Licensing
-
Most countries require you to obtain an Import Export Code (IEC) or trade license.
-
Certain products like food, chemicals, or pharmaceuticals may need additional permits or clearances.
Check your local customs authority or trade ministry for specific requirements.
3. Logistics and Shipping
Plan your transportation and terms using:
-
Freight Forwarders: Professionals who arrange cargo and paperwork.
-
Shipping Methods: Sea (cost-effective), air (fast), or land (regional).
-
Incoterms: Trade terms that define buyer and seller responsibilities (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP).
4. Customs Clearance
Both exporter and importer must clear customs using documents like:
-
Commercial Invoice
-
Packing List
-
Bill of Lading / Airway Bill
-
Certificate of Origin
-
Import/Export License
5. Payment and Currency Management
Trading internationally involves currency fluctuations and financial risks. Common methods include:
-
Letter of Credit (L/C): Bank guarantees payment after terms are met.
-
Advance Payment: Full or partial upfront payment.
-
Open Account: Goods shipped before payment — riskier for sellers.
Common Documents in Import & Export
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Commercial Invoice | Formal bill between buyer and seller |
| Packing List | Detailed contents of the shipment |
| Bill of Lading / Airway Bill | Proof of cargo transfer |
| Certificate of Origin | Declares where goods were manufactured |
| Insurance Certificate | Covers loss or damage in transit |
Benefits of Import and Export for Small Businesses
At NaviExports.com, we emphasize how even small businesses can go global. Here’s how:
-
Access New Markets: Exporting helps increase reach and revenue.
-
Reduce Costs: Importing cheaper raw materials or components can improve margins.
-
Digital Advantage: Tools like online marketplaces and shipping APIs make global trade accessible.
Challenges to Consider
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulations | Navigating different country laws |
| Tariffs and Duties | Can affect pricing and profits |
| Logistics Risks | Includes delays, damage, or theft |
| Currency Fluctuations | Affects the value of transactions |
FAQs About Import and Export
Q1. What’s the difference between import and export?
Import brings goods into your country; export sends goods abroad.
Q2. Can small businesses participate in trade?
Yes! With research, licensing, and planning, even home-based businesses can thrive internationally.
Q3. Are licenses mandatory?
In most countries, yes. Check your national trade portal or customs site.
Q4. What are Incoterms?
Standard global terms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) defining responsibility for shipping, insurance, and delivery.
Q5. How to find international buyers or suppliers?
-
Use B2B directories (Alibaba, Global Sources)
-
Attend trade fairs
-
Join export promotion councils
-
List your company on naviexports.com to boost global visibility
Quick Checklist for Getting Started
✅ Understand what import/export means
✅ Conduct target market and competitor research
✅ Secure trade licenses and certifications
✅ Choose trusted freight/logistics partners
✅ Learn Incoterms and customs documentation
✅ Plan for currency exchange and payment terms
✅ Ensure legal and regulatory compliance
Conclusion
Import and export aren’t just for multinational giants — they’re powerful tools for small businesses, manufacturers, and entrepreneurs. By mastering the basics of import and export, understanding required processes, and connecting with the right partners (like us at NaviExports.com), you can expand globally, reduce costs, and stay competitive.
Whether you’re planning your first shipment or scaling up internationally, the world of trade is open for business. Start exploring today.